1.

#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Circle
{
int radius;
public:
Circle() { radius = 1; }
Circle(int radius) { this->radius = radius; }
int getRadius() { return radius; }
void setRadius(int radius) { this->radius = radius; }
};
void swap(Circle& a, Circle& b) {
int temp = a.getRadius();
a.setRadius(b.getRadius());
b.setRadius(temp);
}
int main()
{
Circle a(10);
Circle b(20);
cout << "a의 반지름 >> " << a.getRadius() << endl;
cout << "b의 반지름 >> " << b.getRadius() << endl;
swap(a, b);
cout << "a의 반지름 >> " << a.getRadius() << endl;
cout << "b의 반지름 >> " << b.getRadius() << endl;
}2.

#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void half(double& a) {
a /= 2;
}
int main() {
double n = 20;
half(n);
cout << n;
}3.

#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
void combine(string t1, string t2, string& t3) {
t3 = t1 + " " + t2;
}
int main() {
string text1("I love you"), text2("very much");
string text3;
combine(text1, text2, text3);
cout << text3;
}4.

#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
bool bigger(int a, int b, int& big) {
big = (a > b) ? a : b;
return a == b ? true : false;
}
int main() {
int a, b, big;
cin >> a >> b;
if (bigger(a, b, big))
cout << "두 수는 같습니다." << endl;
else
cout << "두 수는 다릅니다." << endl;
cout << "더 큰 수는 " << big << "입니다." << endl;
}5.
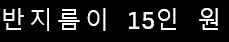
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Circle {
int radius;
public:
Circle(int r) { radius = r; }
int getRadius() { return radius; }
void setRadius(int r) { radius = r; }
void show() { cout << "반지름이 " << radius << "인 원" << endl; }
};
void increaseBy(Circle& a, Circle& b) {
a.setRadius(a.getRadius() + b.getRadius());
}
int main() {
Circle x(10), y(5);
increaseBy(x, y);
x.show();
}6.

#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
char& find(char a[], char c, bool& success) {
for (int i = 0; a[i] != '\0'; i++) {
if (a[i] == c) {
success = true;
return a[i];
}
}
success = false;
}
int main() {
char s[] = "Mike";
bool b = false;
char& loc = find(s, 'M', b);
if (b == false) {
cout << "M을 발견할 수 없다" << endl;
return 0;
}
loc = 'm';
cout << s << endl;
}7.

#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class MyIntStack {
int p[10];
int tos;
public:
MyIntStack();
bool push(int n);
bool pop(int& n);
};
MyIntStack::MyIntStack() {
tos = -1;
}
bool MyIntStack::push(int n) {
if (tos == 10 - 1) // (tos == sizeof(p)/sizeof(p[0]) -1) 도 가능하다
return false;
else {
p[++tos] = n;
return true;
}
}
bool MyIntStack::pop(int& n) {
if (tos == -1)
return false;
else {
n = p[tos--];
return true;
}
}
int main() {
MyIntStack a;
for (int i = 0; i < 11; i++) {
if (a.push(i)) cout << i << ' ';
else cout << endl << i + 1 << " 번째 stack full" << endl;
}
int n;
for (int i = 0; i < 11; i++) {
if (a.pop(n)) cout << n << ' ';
else cout << endl << i + 1 << " 번째 stack emtpy";
}
cout << endl;
}8.

#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class MyIntStack {
int* p;
int size;
int tos;
public:
MyIntStack();
MyIntStack(int size);
MyIntStack(const MyIntStack& s);
~MyIntStack();
bool push(int n);
bool pop(int& n);
};
MyIntStack::MyIntStack() {
tos = -1;
size = 1;
p = new int[size];
}
MyIntStack::MyIntStack(int size) {
this->size = size;
tos = -1;
p = new int[size];
}
MyIntStack::~MyIntStack() {
delete[] p;
}
MyIntStack::MyIntStack(const MyIntStack& s) {
tos = s.tos;
size = s.size;
p = new int[size];
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
p[i] = s.p[i];
}
}
bool MyIntStack::push(int n) {
if (tos == size - 1)
return false;
else {
p[++tos] = n;
return true;
}
}
bool MyIntStack::pop(int& n) {
if (tos == -1)
return false;
else {
n = p[tos--];
return true;
}
}
int main() {
MyIntStack a(10);
a.push(10);
a.push(20);
MyIntStack b = a;
b.push(30);
int n;
a.pop(n);
cout << "스택 a에서 팝한 값 " << n << endl;
b.pop(n);
cout << "스택 b에서 팝한 값 " << n << endl;
}9 return *this;

#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Accumulator {
int value;
public:
Accumulator(int value) { this->value = value; }
Accumulator& add(int n);
int get() { return value; }
};
Accumulator& Accumulator::add(int n) {
value += n;
return *this;
}
int main() {
Accumulator acc(10);
acc.add(5).add(6).add(7); // acc의 value 멤버가 28이 된다.
cout << acc.get() << endl; // 28 출력
}10.

#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Buffer {
string text;
public:
Buffer(string text) { this->text = text; }
void add(string next) { text += next; }
void print() { cout << text << endl; }
};
Buffer& append(Buffer &buf, string text) {
buf.add(text);
return buf;
}
int main() {
Buffer buf("Hello");
Buffer& temp = append(buf, "Guys");
temp.print();
buf.print();
}'C++' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [명품 C++ Programming] 7장 실습 문제 (0) | 2025.05.24 |
|---|---|
| [명품 C++ Programming] 6장 실습 문제 (0) | 2025.04.28 |
| [명품 C++ Programming] 3장 실습 문제 (1) | 2025.04.26 |
| [명품 C++ Programming] 3장 Open Challenge (지수 표현 클래스 만들기) (0) | 2025.04.26 |
| [명품 C++ Programming] 4장 실습 문제 (0) | 2025.04.08 |